Shallow slow earthquakes to decipher future catastrophic earthquakes in the Guerrero seismic gap
Abstract
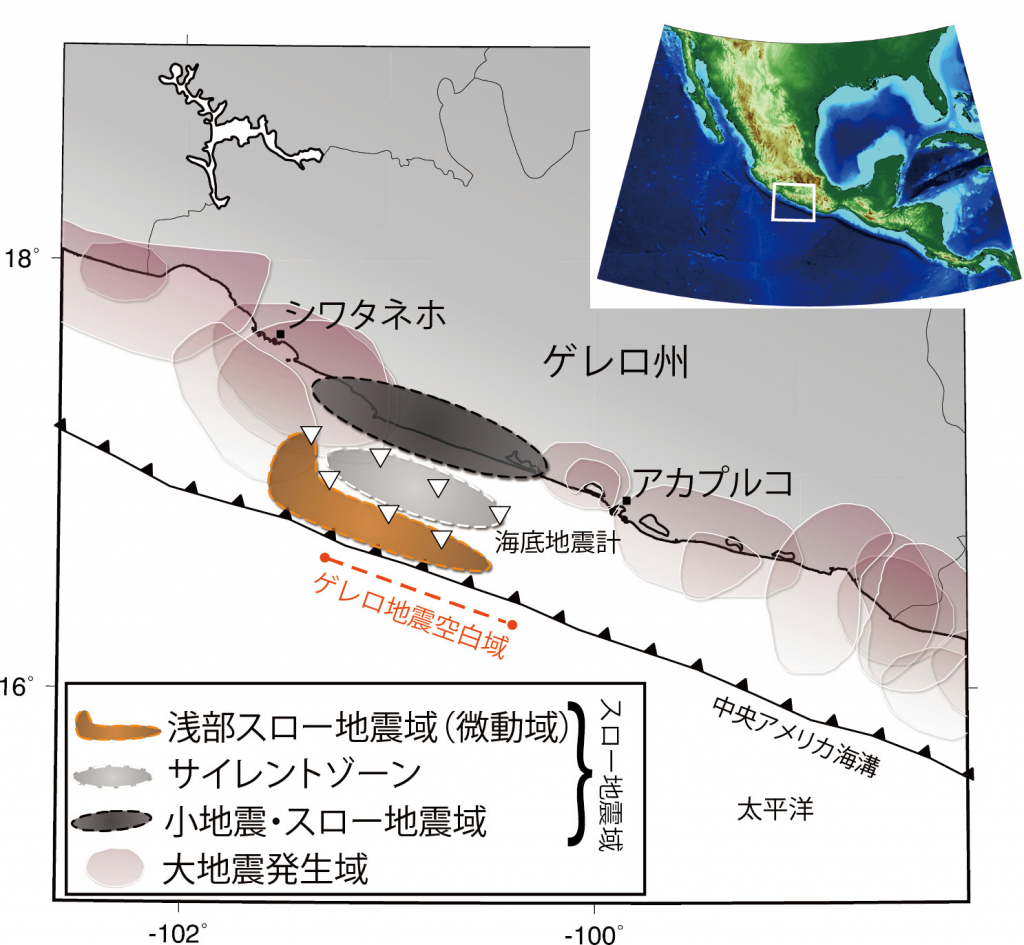
The Guerrero seismic gap is presumed to be a major source of seismic and tsunami hazard along the Mexican subduction zone. Until recently, there were limited observations at the shallow portion of the plate interface offshore Guerrero, so we deployed instruments there to better characterize the extent of the seismogenic zone. Here we report the discovery of episodic shallow tremors and potential slow slip events in Guerrero offshore. Their distribution, together with that of repeating earthquakes, seismicity, residual gravity and bathymetry, suggest that a portion of the shallow plate interface in the gap undergoes stable slip. This mechanical condition may not only explain the long return period of large earthquakes inside the gap, but also reveals why the rupture from past M < 8 earthquakes on adjacent megathrust segments did not propagate into the gap to result in much larger events. However, dynamic rupture effects could drive one of these nearby earthquakes to break through the entire Guerrero seismic gap.